Imagine a world where quality healthcare is just a click away. That’s the revolutionary promise of using telemedicine in our digital age – an era where convenience is desired and a fundamental expectation.
Healthcare has boldly stepped out of the confines of sterile clinic environments, bringing forth telemedicine as a groundbreaking confluence of technology and patient care. It isn’t about supplanting the time-honored practice of in-person healthcare but augmenting it. It’s about bringing critical medical services to the fingertips of individuals in distant corners of the world, those restricted by physical limitations, and the busy bees who demand flexibility.
The criticality of telemedicine came into sharp focus during global situations such as the COVID-19 pandemic, showcasing its necessity as a tool to maintain continuous healthcare provision when face-to-face encounters represented potential risks. According to a report by Fortune Business Insights, the global telemedicine market size was USD 87.41 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 286.22 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 17.2% during the forecast period.
We will navigate the crucial components, ally with cutting-edge technologies, and operate practical prototypes to empower you with the insight required to redefine healthcare delivery within your realms.
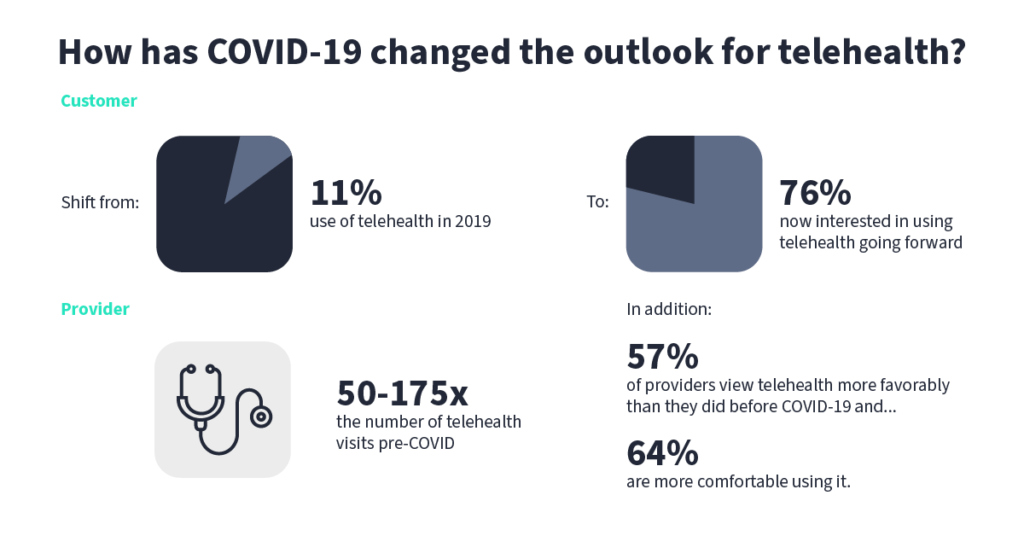
Understanding the Telehealth Landscape in 2023
For many, especially during the peak of the pandemic, telemedicine became the primary care method. Accenture reported that 77% of patients consider access to care more important than in-person visits with healthcare providers.
However, the telemedicine landscape is not a monolith; it’s a vibrant ecosystem teeming with various forms of technology, diverse patient needs, regulatory frameworks, and a tapestry of healthcare providers. It encompasses synchronous solutions.
At its core, a solidly built telemedicine platform includes:
- video conferencing technology, enabling real-time patient-provider consultations;
- an integrated scheduling system, streamlining appointments;
- prescription management tools;
- and secure messaging features, facilitating direct communication while ensuring privacy.
Furthermore, integrating Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is vital, allowing seamless patient data access and informing better healthcare decisions. All these parts must fit together just right, making a complete system that puts health and ease first.
Regulatory considerations and compliance (HIPAA & GDPR)
In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) delineates the protocol for safeguarding sensitive patient data. For instance, the HIPAA Security Rule requires healthcare providers to conduct risk assessments and establish a risk management policy, among other actions, to help protect patients’ electronic health information. This necessity is underscored by the 2021 Healthcare Breach Report by Bitglass, which found 599 healthcare breaches of protected health information in the previous year, representing a 55.1% increase from a year earlier.
In Europe, or for those handling European patients’ data, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes rigorous data protection standards. This regulation is particularly vital given the surge in the popularity of telemedicine, with the European healthcare market experiencing significant growth in digital services. Under the GDPR, compliance is non-negotiable, as failure to adhere can result in substantial penalties – up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
These strict standards underscore the necessity for robust data protection measures, especially in the wake of notable global data breaches in various sectors. We’ve also discussed these regulations in depth in our Master the HealthTech guide. Non-compliance risks these financial penalties and can inflict irreparable harm to an organization’s reputation, a critical concern in a health industry increasingly reliant on digital trust.
The significance of patient and provider experience
The success of any telemedicine platform hinges on the experiences of both patients and healthcare providers.
For patients, the platform should be convenient, reducing the need for physical travel and wait times while offering easy access to healthcare professionals and services.
For providers, the platform’s intuitive design should simplify workflow, reduce administrative burdens, and facilitate efficient care delivery.
Achieving this delicate balance is where user experience converges with operational practicality, creating a harmonious system that enhances healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
Developing a Secure Telemedicine Platform
Data encryption
Implementing end-to-end encryption is non-negotiable when handling patient data. This means that information is encrypted from the moment it leaves the sender until it reaches the intended recipient, making it unreadable to any prying eyes in between.
By ensuring that data-in-transit and data-at-rest are encrypted using the latest standards, telemedicine software can provide the security electronic health records demand, keeping cybercriminals at bay and trust intact.
Identity verification and access management
Robust identity verification measures should be in place to ensure that individuals are who they claim to be, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This might include multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, or unique access codes.
Additionally, access management policies need to be stringent. Only some require full access to all information; permissions should be based on roles and the minimum necessary information to fulfill those roles. This principle limits exposure and helps contain potential breaches, ensuring that telemedicine becomes a reliable form of remote clinical services.
Regular security audits and compliance checks
Complacency can be a silent predator in security. Regular security audits and compliance checks are essential preventive medicine. These audits assess and ensure all systems and processes adhere to the latest security standards and regulations. They identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, providing the platform stays one step ahead of cyber threats.
Moreover, compliance checks ensure that the platform remains in line with legal requirements, a critical aspect considering the evolving nature of cybersecurity laws, especially when offering health services.
Handling medical records
Medical records are not mere data; they’re a digital extension of the patient’s health. Ensuring their confidentiality is as crucial as maintaining their integrity, just as it would be for electronic medical records. Any alteration in data – intentional or not – can have serious repercussions.
Hence, secure storage solutions, checksums, and digital signatures should be employed to maintain data integrity. Regular backups and a reliable recovery system must also be in place to prevent data loss and ensure continuity of care.
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning
Hope for the best, but prepare for the worst – this adage holds significant weight in digital healthcare provision. A solid disaster recovery plan is like a digital fire escape, providing a clear pathway out during emergencies like data breaches or system failures and safeguarding the telemedicine platform.
It outlines the steps to be taken to recover critical systems and data quickly. Complementing this, business continuity planning ensures that the essential services of the telemedicine platform can continue operating smoothly during and after a crisis, mitigating disruptions in patient care.
Building a secure telemedicine service isn't just about strong encryption and tight access controls; it's about creating a complete environment of trust. I cannot overemphasize the importance of a holistic approach. Even the most secure system isn't enough if its design is so complicated that users are tempted to find less secure workarounds.
Designing for Intuitiveness and User Engagement
User-Centric Design
In the digital health sphere, a user-centric approach isn’t just beneficial for telemedicine; it’s essential for all telehealth platforms. Telehealth platforms must be designed with an empathetic lens, prioritizing the ease of use for all users – patients and healthcare providers alike in 2023.
This involves a clean, intuitive interface with straightforward navigation, quick loading times, and easy-to-understand instructions. Accessibility in HealthTech should also be a key focus, ensuring the platform is usable for people with disabilities, thus not alienating any user group. Collecting and incorporating user feedback is crucial in this iterative process, ensuring the platform meets and exceeds user expectations.
Enhancing patient-provider communication
Effective communication forms the backbone of exemplary healthcare. Telemedicine platforms should facilitate this by offering seamless, real-time consultation between patients and providers. Features like instant messaging, video conferencing, and easy appointment scheduling, all integrated within a secure environment, can significantly enhance communication.
A platform that supports the sharing of lab results, images, or medical records, with patient consent, can further enrich this dialogue. Such transparent and efficient communication can foster a stronger patient-provider relationship, a cornerstone in healthcare.
Mobile responsiveness and cross-platform compatibility
Like a mobile app, a telehealth platform must be responsive, ensuring users have a consistent experience across devices.
Moreover, cross-platform compatibility ensures broader accessibility, meaning the platform functions flawlessly across different operating systems. This ubiquity improves user engagement and positions the platform as an adaptable and reliable healthcare companion.
Incorporating AI and ML for improved service delivery
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are more than just buzzwords; they’re tools that provide information and put telemedicine into new dimensions of health outcomes.
From intelligent chatbots that provide immediate responses to patient queries to predictive analytics that personalize patient care, these technologies enhance service delivery. They can automate routine tasks, provide data-driven insights, and support decision-making processes, ultimately improving health outcomes and user satisfaction.
Creating an intuitive telemedicine platform mirrors the warmth and ease of face-to-face healthcare interactions. As designers, our role is steeped in empathy; we're not just structuring a platform but shaping a comforting, accessible digital health journey. Every feature must resonate with trust and simplicity, amplifying the human aspect of healthcare even in a virtual realm.
Challenges and Solutions in Telemedicine Deployment
While the benefits are transformative, the path is interspersed with significant challenges that health systems must navigate. These hurdles range from technological and cybersecurity issues to legal intricacies and resistance from traditional healthcare practitioners and patients.
However, with every challenge comes an opportunity to innovate and strengthen the system. This section delves into the everyday difficulties encountered during healthcare software development. It explores practical solutions, equipping healthcare leaders with the knowledge to address potential setbacks preemptively and smoothly operationalize their telemedicine initiatives.
Overcoming resistance to change
For generations, healthcare has been characterized by in-person interactions and the sudden shift to telemedicine solutions can be met with skepticism and resistance from both healthcare providers and patients. This reluctance can stem from discomfort with new technology, concerns about the quality of care services, or simply an ingrained preference for face-to-face consultation.
Healthcare professionals might worry about potential malpractice risks, the impersonal nature of remote patient visits, or technical challenges. Meanwhile, patients may have concerns about the security of their health data, the ability to communicate effectively with their providers via technology, or even the fear of being marginalized by automated systems.
Continuing medical education and communication are crucial to overcoming this resistance. This could mean organizing workshops highlighting the benefits of telemedicine for healthcare professionals, such as reaching remote or immobile patients and reducing overhead costs. Hands-on training sessions can alleviate discomfort with the technology, while peer testimonials and pilot programs can demonstrate real-world success stories.
For patients, creating user-friendly platforms, providing resources that answer common questions, and offering technical support can help ease the transition. It’s also important to reassure patients that telemedicine is an option, not a mandatory replacement for in-person care and that their comfort and quality of care are priorities.
Change management strategies should also include feedback mechanisms that allow users to share their experiences, concerns, and suggestions for improvement. This feedback can facilitate continuous refinement of the telemedicine services and make users feel heard and valued, increasing their willingness to embrace the new system.
Ensuring technological reliability and uptime
Users must trust that the platform will be available and reliable whenever required, especially in emergencies. Any form of technological failure not only undermines this trust but can also have serious consequences when urgent medical services are needed.
Ensuring reliability and uptime requires a robust technological infrastructure. This involves reliable hosting services with solid service level agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing high uptime percentages. Redundant systems and backups should be in place to keep the platform running even if one component fails. Additionally, edge computing can enhance the speed and reliability of services for users across various geographical locations.
Continuously monitoring the system for potential issues is just as important. This can be achieved through automated alerts that notify the technical team of system slowdowns or outages. Regular load testing can help anticipate and manage increased user numbers, especially during public health crises or natural disasters when telemedicine services might be in higher demand.
Having a dedicated technical support team available 24/7 is also essential. They can quickly address and resolve user issues, reducing downtime and maintaining the platform’s reliability. Furthermore, clear communication with users about any expected downtime for system maintenance or updates helps manage expectations and maintain trust.
Strategies for multifaceted cybersecurity threats
Cybersecurity threats loom as omnipresent shadows over technological advancements. Due to the nature of their services and the workflow they support, telehealth platforms have become prime targets for cybercriminals. These threats are multifaceted — from data breaches and ransomware attacks to phishing scams and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
A multi-layered, proactive security strategy is essential to safeguard telemedicine and telehealth services against these threats. Here are several critical components of such a strategy:
- End-to-end encryption. All data should be encrypted using robust and up-to-date encryption methods, whether at rest or in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and secure. Updating encryption standards is crucial, as outdated encryption can be an easy target for cybercriminals.
- Regular cybersecurity training. Human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Traditional training programs for all healthcare staff and administrators can fortify this link. These programs should educate about the importance of strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and following proper security protocols. An informed team is a crucial line of defense against cyber threats.
- Advanced threat detection. Employing advanced AI and machine learning algorithms can help detect unusual data patterns or system vulnerabilities that may indicate a cybersecurity threat. Early detection is critical to preventing potential breaches.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to access the system, making it harder for unauthorized users to break in.
- Regular system updates and patch management. Cybersecurity is a moving target, constantly emerging new threats. Periodic system updates and patches are necessary to fix security vulnerabilities. An outdated system is a playground for cybercriminals.
- Incident response plan. Despite all precautions, breaches can still occur. An incident response plan is a structured approach detailing the procedures to follow when a cyber incident occurs. This plan should include immediate steps to control the breach, communication strategies, and measures to prevent future incidents. Regular drills to practice responding to a cyber incident can ensure swift and effective action when needed most.
- Legal compliance and data privacy regulations. You need to ensure the patient can get medical consultations securely. Compliance with national and international cybersecurity and data privacy regulations is non-negotiable. These laws provide a framework for necessary security measures and protect patients’ rights during data breaches.
- Cybersecurity insurance. As an added layer of protection, cybersecurity insurance can help cover the financial losses resulting from cyber-attacks. While this doesn’t prevent attacks, it provides a safety net in the aftermath.
By integrating these strategies, telemedicine platforms can fortify themselves against the ever-evolving threat of cyber attacks, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive health data and services.
Contact
Would you like to discuss how the development of telehealth may grow your business?
Embracing the Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Continuous innovation will be essential in 2024 and the future. Integrating emerging technologies, adapting to new healthcare challenges, and listening to user feedback are crucial steps in this ongoing journey. Telehealth has opened new horizons in healthcare, making services more accessible, efficient, and patient-friendly. However, its success relies on a collaborative approach, where feedback drives improvement, technology complements human expertise, and security is a shared responsibility.
This is an opportunity for enterprises venturing into telemedicine to make a profound impact. It’s about extending the reach of quality healthcare, breaking down geographical and logistical barriers, and, most importantly, creating a system where technology empowers healthcare providers and patients. As we tread this path, our collective experiences, learnings, and innovations will shape tomorrow’s healthcare.